Product description:
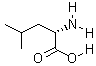
English name: L-Leucine
Molecular formula: C6H13NO2
Molecular weight: 131.17
Introduction: L-leucine, also known as leucine, chemically called a monoamino-isocaproic acid, was first isolated by Proust in 1819 from cheese, and later Braconnot crystallized from acid hydrolysates of muscle and wool, and named leucine. L-leucine is one of the 18 common amino acids, and is called Branched chain amina acids (BCAA) because the molecular structure of L-leucine, L-isoleucine, and L-oxine contains a methyl side chain.
Shape: It is white crystal or crystalline powder, a kind of non-polar amino acid, slightly bitter in taste, soluble in water, solubility at 20℃ and 25℃ respectively 23.7g /L and 24.26g /L, acetic acid (10.9g/L), dilute hydrochloric acid, alkali solution and carbonate solution, slightly soluble in alcohol (0.72g /L), insoluble in ether. Sublimation when heated to 145^r 148℃, decomposition at 293-295 0C, specific gravity 1.29 (180C), specific rotation [a] D20 + 14.5 ^-+ 16.0 (6mo1/L Hcl, C=1), isoelectric point 5.98. |
 CN
China Suppliers > lifengchem >
CN
China Suppliers > lifengchem >