Rutin
-
- Category :
Pharmaceuticals and Biochemicals
- CAS NO : 153-18-4
- EC NO : 205-814-1
- Molecular Formula : C27H30O16
- Main Specifications :
- Synonyms : C.I. 75730;(+)-Rutin Hydrate;Quercetin-3-rutinoside;Vitamin P;2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 6-O-(6-deoxyhexopyranosyl)hexopyranoside;2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 6-O-(6-deoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl)-D-glucopyranoside;Rutin NF12;Rutin extract;Sophora Japonica Extract;Rurin Sophora Japonica Extract;
Molecular Structure:
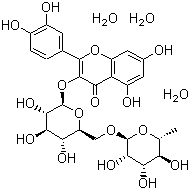
Product description:
Product Name: Rutin
Synonyms: C.I. 75730; Rutin [JAN]; (+)-Rutin Hydrate; Quercetin-3-rutinoside~Vitamin P; 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 6-O-(6-deoxyhexopyranosyl)hexopyranoside; 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 6-O-(6-deoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl)-D-glucopyranoside
CAS RN.: 153-18-4
EINECS: 205-814-1
Molecular Weight: 610.5175
Molecular Formula: C27H30O16
Melting Point(℃): 195℃
Water Solubility: 12.5 g/100 mL
Molecular Structure:
Appearance & Color: Yellow to greenish yellow powder
Solubility: Practically insoluble in chloroform ether, and cold water
Product Specification: 95.0 ~ 101.5% Rutin EP/USP/BP/NF
Product Introduction
Rutin, also called rutoside, quercetin-3-rutinoside and sophorin, is a citrus flavonoid glycoside found in the flower bud of Scphora japonica L, It is also present in many other plants and sometimes referred to as Vitamin P, although not strictly a vitamin.
Rutin is the glycoside between the flavonol quercetin and the disaccharide rutinose. Rutin can be created by bonding a disaccharide onto the hydroxyl group of Quercetin. Rutin (quercetin rutinoside), as well as quercitrin, is a glycoside of the flavonoid Quercetin. As such, the chemical structure of both is very similar, with the difference existing in the Hydroxyl functional group. Both quercetin and rutin are used in many countries as medications for blood vessel protection and are ingredients of numerous multivitamin preparations and herbal remedies.
Product Functions
1. Rutin inhibits platelet aggregation, as well as decreasing capillary permeability, making the blood thinner and improving circulation.
2. Rutin has anti-inflammatory activity.
3. Rutin inhibits aldose reductase activity. Aldose reductase is an enzyme normally present in the eye and elsewhere in the body. It helps change glucose into a sugar alcohol called sorbitol.
4. Rutin also strengthens the capillaries, and, therefore, can reduce the symptoms of haemophilia. It also may help to prevent a common unpleasant-looking venous edema of the legs. Rutin, as ferulic acid, can reduce the cytotoxicity of oxidized LDL cholesterol and lower the risk of heart disease.
5. There is also some evidence that Rutin can be used to treat hemorrhoids, varicosis, and microangiopathy.
6. Rutin is also an antioxidant, along with quercetin, acacetin, morin, hispidulin, hesperidin, and naringin; it was found to be the strongest.
7. are used in the treatment of chronic venous insufficiency.
Applications
● Pharmaceutical stuff
● Functional food and food additive
