Carmustine
-
- Category :
Pharmaceuticals and Biochemicals
- CAS NO : 154-93-8
- EC NO : 205-838-2
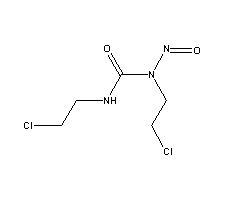
- Molecular Formula : C5H9Cl2N3O2
- Main Specifications : 96.0-101.0% up, medical grade
- Synonyms : 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitroso-urea;Carmustin;
Package: 25kg/drum
Uses : 96.0-101.0% up, medical grade
Molecular Structure:
Product description:
Function of Carmustine
Carmustine is a nitrosourea alkylating agent. Although it has a chloroethyl group in its structure, its chemical reaction is different from that of nitrogen mustard. Because it can penetrate the blood-brain barrier, it is often used for brain tumors and intracranial metastases.
It is now believed that this product forms isocyanate and diazonium hydroxide through the action of OH- ions under physiological conditions after entering the body. Isocyanates carbamylate proteins, and diazonium hydroxide generates carbanion ions to alkylate biological macromolecules. Isocyanate can inhibit DNA polymerase, inhibit DNA repair and RNA synthesis. This product is a periodic non-specific drug, and it is not completely cross-resistant with general alkylating agents. The resistance of nitrite drugs has little to do with multi-drug resistance genes. This product has high fat solubility. Permeable to the blood-brain barrier, the concentration in cerebrospinal fluid is 50% to 70% of the plasma concentration. It is mainly metabolized in the liver. The metabolites stay in the plasma for several days and still have anticancer effects. They are slowly released after binding to the protein and have a lasting effect.
