Green tea extract
-
- Category :
Agrochemicals
- CAS NO : 989-51-5
- EC NO : 283-519-7
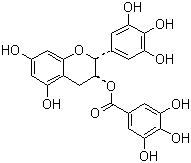
- Molecular Formula : C22H18O11
- Main Specifications : Tea polyphenol 20%-98% by UV
- Synonyms : EGCG;(2R,3R)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3-yl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate;Green Tea Extract Powder;;Green Tea;Green Tea P.E;Green Tea Extract;Green tea extract Polyphenols;Green tee extract;Tea Polyphenols;Tea polyphenol;Tea Polyphenol (TP98);Epigallocatechin gallate;
Package: 25kg/drum
Uses : Application of tea polyphenols in the industry of daily chemicals In general, most cosmetics contain oil, wax, hydrocarbon and surface active agent, all that easily react to oxygen in air and produce peroxidant, acids, aldehydes etc.
Molecular Structure:
Product description:
Function of Green tea extract
Green tea extract, like many herbs, is standardized in the production phase to guarantee that a certain percentage of the active ingredients remain present in the final capsulized form. The active ingredients in green tea extract are polyphenols in the form of flavonoids like catechins and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). Polyphenols, flavonoids, catechins and EGCG are powerful antioxidants that appear to interfere with and reduce the spread of certain types of cancer cells. The antioxidant activity of EGCG in green tea extract powder is purportedly up to 100 times more powerful than that of vitamin C or E.
(1)Application of tea polyphenols in the industry of medicine
Tea polyphenols can protect easy-oxidant in the body from oxidizing through oxidized itself to made cellular activity normalize.
(2)Application of tea polyphenols in food industry
The fat in food is easy to oxidize itself to produce free radicals. Tea polyphenols can supply lots of protons, which combine with over 98% of these free radicals, thereby stop next chemical reaction and protect the fat from further oxidizing.
(3)Application of tea polyphenols in the industry of daily chemicals
In general, most cosmetics contain oil, wax, hydrocarbon and surface active agent, all that easily react to oxygen in air and produce peroxidant, acids, aldehydes etc.
