Levetiracetam
-
- Category :
Pharmaceuticals and Biochemicals
- CAS NO : 102767-28-2
- EC NO :
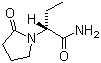
- Molecular Formula : C8H14N2O2
- Main Specifications : 99% up
- Synonyms : (s)-2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamide;(S)-1-pyrrolidineacetamid;(+-)-alpha-Ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidineacetamide;(S)-alpha-Ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidineacetamide;1-Pyrrolidineacetamide;alpha-ethyl-2-oxo-;alpha-Ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidineacetamide;Etiracetamum [INN-Latin];Keppra;Levetiracetam [INN];Levetiracetamum [INN-Latin];LEVITIRACETAM;UCB 6474;UCB-6474;UCB-L 059;Name:(S)-2-(2-Oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamide (Levetiracetam);(2R)-2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamide;(2S)-2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamide;Levetiracetame;
Package: 25kg/drum
Uses : is a medication used to treat epilepsy
Molecular Structure:
Product description:
Function of Levetiracetam
Levetiracetam, marketed under the trade names Keppra among others, is a medication used to
treat epilepsy. It is used for partial onset, myoclonic, or tonic-clonic seizures. It is the S-enantiomer
of etiracetam.
Levetiracetam is available by mouth in two forms: immediate release and extended release.[3] It is
also available by injection. An immediate release tablet has been available as a generic in the
United States since November 2008, and in the UK since 2011. The United States patent for the
extended release tablet will expire on September 17, 2028. It was initially patented by UCB Pharma.
Application of Levetiracetam
Levetiracetam has been approved in the United States as add-on treatment for partial (focal),
myoclonic, and tonic-clonic seizures. Levetiracetam has been approved in the European Union
as a monotherapy treatment for epilepsy in the case of partial seizures, or as an adjunctive
therapy for partial, myoclonic, and tonic-clonic seizures. Levetiracetam has been shown to reduce
partial (focal) seizures by 50% or more as an add-on medication. It is also used in veterinary
medicine for similar purposes.
Levetiracetam is sometimes used off-label to treat status epilepticus or to prevent seizures
associated with subarachnoid hemorrhages.
Levetiracetam has potential benefits for other psychiatric and neurologic conditions such as
Tourette syndrome,anxiety disorder,[and Alzheimer's disease.However, its most serious adverse
effects are behavioral, and its benefit-risk ratio in these conditions is not well understood.
Levetiracetam has not been found to be useful for treatment of neuropathic pain,nor for
treatment of essential tremors.Levetiracetam has not been found to be useful for treating autism,
but is an effective treatment for partial, myoclonic, or tonic-clonic seizures associated with
autism spectrum disorder.
