Polymyxin B Sulphate
-
- Category :
Pharmaceuticals and Biochemicals
- CAS NO : 1405-20-5
- EC NO : 215-774-7
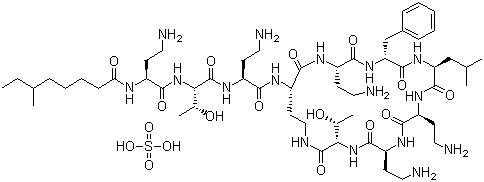
- Molecular Formula : C48H84N16O17S
- Main Specifications : 6500IU/MG up /Medicine Grade
- Synonyms : polymyxin B sulfate;Polymyxin B sulfate salt;Polymyxin B Sulphate;Polymyxin B sulfate;Polymyxin B 2,5-SULFATE;Polymyxin B (PMB);N-[3-amino-1-[[1-[[3-amino-1-[[6,9,18-tris(2-aminoethyl)-15-benzyl-3-(1-hydroxyethyl)-12-isobutyl-2,5,8,11,14,17,20-heptaoxo-1,4,7,10,13,16,19-heptazacyclotricos-21-yl]carbamoyl]propyl]carbamoyl]-2-hydroxy-propyl]carbamoyl]propyl]-6-methyl-octanamide,sulfuric acid;N~2~-[4-amino-2-(formylamino)butanoyl]-N-(3-amino-1-{[6,9,18-tris(2-aminoethyl)-15-benzyl-3-(2-hydroxyethyl)-12-(2-methylpropyl)-2,5,8,11,14,17,20-heptaoxo-1,4,7,10,13,16,19-heptaazacyclotricosan-21-yl]carbamoyl}propyl)homoserinamide sulfate (salt);Aerosporin;Polimixin B Sulphate;
Package: 25kg/drum
Uses : bacteremia, endocarditis, pneumonia, post-burn infections, etc.
Molecular Structure:
Product description:
Function of Polymyxin B Sulphate
Polymyxin B sulphate is similar to polymyxin E. It can inhibit gram-negative bacilli such as Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Para Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acidophilus, Pertussis and Shigella, etc. Or bactericidal effect. It is mainly used for Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other Pseudomonas to cause the wounds, urinary tract, eyes, ears, trachea and other parts of the Chemicalbook infection. It can also be used for sepsis and peritonitis. And resistant to aminoglycosides, resistant to third-generation cephalosporin bacteria and Pseudomonas aeruginosa or other sensitive bacteria caused by serious infections, such as bacteremia, endocarditis, pneumonia, post-burn infections, etc.
Polymyxin B is a peptide antibiotic against gram-negative bacilli, which can change the membrane structure to leak small molecules and inhibit the growth of gram-negative bacteria. Has a bactericidal effect on E. coli Chemicalbook. Binds to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Inducing small holes in the outer cell membrane. Mode of action: Combine and interfere with the permeability of the cell plasma membrane. Antibacterial spectrum: Gram-negative bacteria.
