- Category :
Other Chemicals
- CAS NO : 1132-61-2
- EC NO : 214-478-5
- Molecular Formula : C7H15NO4S
- Main Specifications : White Powder
- Synonyms : 3-(4-Morpholino)propanesulphonic acid;3-(N-Morpholino)propanesulfonic acid;3-N-morpholinopropansulfonic acid;MOPS;MOPS, CONCENTRATE SOLUTION;MORPHOLINOPROPANE SULFONIC ACID;TIMTEC-BB SBB009133;LABOTEST-BB LT00455082;LABOTEST-BB LT01595956;4-MORPHOLINEPROPANESULFONIC ACID;4-(MORPHOLINOPROPANE SULFONIC ACID);3-(morpholin-4-yl)propane-1-sulfonic acid;3-(4-Morpholino)propane sulfonic acid;3-MorpholinopropanesuIfonic Acid;
Package: 500g/bottle
Uses : Biological buffer
Molecular Structure:
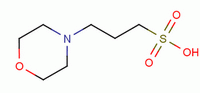
Product description:
The Chinese name of MOPS buffer is 3- (N-morpholinyl) propanesulfonic acid, which belongs to the zwitterionic buffer. It appears as a white powder and has high hydrophilicity and excellent water solubility (1000g/L at 20 ℃). The appearance of dissolved MOPS in aqueous solution is also colorless. The pKa value of MOPS at 25 ° C is 7.14, effectively regulating the pH range from 6.5 to 7.9. Therefore, MOPS is commonly used in molecular biology and biochemical research.
The main application areas of MOPS as a buffer are as follows:
(1) In vitro diagnosis: biochemical kit, DNA/RNA extraction kit, and PCR kit.
(2) Protein/nucleic acid separation and purification: separation in the electrophoresis of nucleic acid and protein, denaturing gel electrophoresis of RNA1, and protein purification in chromatography.
(3) Cell culture medium: The buffer system of the culture medium.
(4) Biosynthesis: A buffer used in biosynthesis.
(5) Measure absorption in UV/visible spectrophotometry and study redox characteristics using cyclic voltammetry.
(6) When controlling the pH of the culture medium at 5, including cell culture media for yeast, bacterial, and mammalian cells.
Precautions when using MOPS buffer:
1. When using MOPS buffer for mammalian cell culture, the concentration of MOPS should not exceed 20mm;
2. There is almost no complexation between MOPS and metals, but once complexation occurs, it may cause interference;
3. MOPS can affect the thickness and barrier performance of the endothelial surface layer in rats;
4. In the presence of glucose, MOPS undergoes partial degradation during high-pressure sterilization.
5. MOPS interacts with DNA and forms complexes;
6. MOPS can alter lipid interactions;
 CN ChemNet > Gold Suppliers > Hubei new DE sheng material science and technology co., LTD. >
CN ChemNet > Gold Suppliers > Hubei new DE sheng material science and technology co., LTD. > 