Adenosine 5'-monophosphate disodium salt
-
- Category :
Inorganic chemicals/Inorganic salts
- CAS NO : 4578-31-8
- EC NO : 224-961-2
- Molecular Formula : C10H12N5Na2O7P
- Main Specifications : 99%
- Synonyms : 5'-Adenylic acid, sodium salt, hydrate;disodium 5'-O-phosphonatoadenosine;Adenosine Monophosphate Disodiium;Adenosine 5'-monophosphoric acid disodium salt;Adenosine 5'-monophosphoric acid disodium salt (AMP);Disodium adenosine 5-phosphate;Adenosine-5'-monophosphate disodium salt;Adenosine 5'-monophosphate disodium salt;5'-Adenosine Monophosphate Disodium Salt;Disodium adenosine 5'-phosphate;
Package: 25kg/drum
Molecular Structure:
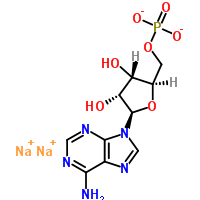
Product description:
1, nucleotide, as a new type of feed additives.Research shows that in the early stage in aquaculture development can promote growth, through the incubation thoroughbred, strengthen the juvenile fish quality, change of intestinal structure, increasing stress tolerance and adjust the congenital and acquired immune response.Also enhanced resistance to viruses, bacteria and parasite infection.
2, in the role of livestock poultry.Add nucleotide, appropriately to maintain animal immune system functioning, promote gastrointestinal development, improving liver function and had important effect on lipid metabolism and so on.Nucleotide is added in the pig or poultry feed can promote growth, improve feed utilization, enhance the ability of resistance and improve meat quality.
3, nucleotides as plant growth stimulator has a great potential for use.Studies have shown that the transforming ability of nucleotides can improve seed inclusions, germination rate and seedling quality, promote the production of plant roots, and increase chlorophyll content, can deepen leaf color of rice, apple, corn, soybean, rapeseed, citrus fruits and other crops were to increase production and precocious effect.
4.Can be used as feed additives.
5. Feeding animal meat with the product can compare with wild animal meat quality.No drug residues, no antibiotics.After is the domestic development of a kind of trend of resistance breeding.
 CN
ChemNet > Gold Suppliers > Tianjin Fairtrade Biopharma Co.,Ltd. >
CN
ChemNet > Gold Suppliers > Tianjin Fairtrade Biopharma Co.,Ltd. > 