Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone Suppliers, Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone Manufacturers.
Hunan Huacheng Biotech,Inc.

Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone
Category :
Pharmaceuticals and BiochemicalsSynonyms :
neohesperidin dihydrochalcone from*citrus fruit;Neosperidin dihydrochalcone;3,5-dihydroxy-4-[3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)propanoyl]phenyl 2-O-(6-deoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl)-beta-D-glucopyranoside;CAS NO :
20702-77-6EC NO :
243-978-6Molecular Formula :
C28H36O15Molecular Weight :
612.5764Main Specifications :
InChI :
InChI=1/C28H36O15/c1-11-21(34)23(36)25(38)27(40-11)43-26-24(37)22(35)19(10-29)42-28(26)41-13-8-16(32)20(17(33)9-13)14(30)5-3-12-4-6-18(39-2)15(31)7-12/h4,6-9,11,19,21-29,31-38H,3,5,10H2,1-2H3/t11-,19+,21-,22+,23+,24-,25+,26+,27-,28+/m0/s1Product description :
Product Name:Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone
Botanical Name:Citrus aurantium
Part Used: Fruit
Application: Natural Sweetener
Brief Info:1-99%
.....................................................................................................................................
Active Ingredient:Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone
CAS No.:20702-77-6
M.Formula: C28H36O15
M.Weight:612.58
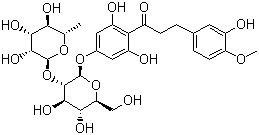
Structural formula:

.....................................................................................................................................
Specification
(1)1-99% Neohesperidosyl dihydrochalcone
.....................................................................................................................................
Description
Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone, sometimes abbreviated to neohesperidin
DC or simply NHDC, is an artificial sweetener derived from citrus.
NHDC was discovered during the 1960s as part of a United States Department
of Agriculture research program to find methods for minimizing the taste of bitter
flavorants in citrus juices. Neohesperidin is one such bitter compound. When
treated with potassium hydroxide or another strong base, and then catalytically
hydrogenated, it becomes NHDC, a compound roughly 15001800 times
sweeterthan sugar at threshold concentrations; around 340 times sweeter than
sugar weightfor weight. Its potency is naturally affected by such factors as the
application in which it is used, and the pH of the product.Like other highly sweet
glycosides, such as glycyrrhizin and those found in stevia, NHDC's sweet taste
has a slower onset than sugar's and lingers in the mouth for some time.
Unlike aspartame, NHDC is stable to elevated temperatures and to acidic or basic
conditions, and so can be used in applications that require a long shelf life.
NHDC itself can stay foodsafe for up to five years when stored in optimal conditions.
The European Union approved NHDC's use as a sweetener in 1994. It has
not been approved as a sweetener in the United States. It is sometimes said
that NHDC is considered a Generally Recognized as Safe flavour enhancer
by the Flavour and Extract Manufacturers' Association, which is a trade group
with no legal standing. NHDC has never appeared on the FDA's GRAS listing.
It is particularly effective in masking the bitter tastes of other compounds found
in citrus, including limonin and naringin. Industrially, it is produced by extracting
neohesperidin from the bitter orange, and then hydrogenating this to make NHDC.
The product is well known for having a strong synergistic effect when used in
conjunction with other artificial sweeteners such as aspartame, saccharin,
acesulfame potassium, and cyclamate, as well as sugar alcohols such as
xylitol. NHDC usage boosts the effects of these sweeteners at lower concentrations
than would otherwise be required; smaller amounts of other sweeteners are needed.
This provides a cost benefit.
As a flavour enhancer, NHDC is used in a wide range of products and is indicated
by the E number E 959. It is noted particularly for enhancing sensory effects (known
in the industry as 'mouth feel'). An example of this is 'creaminess' in dairy foods
such as yogurt and ice cream, but is also widely favoured for use in otherwise
naturally bitter products. Pharmaceutical companies are fond of the product as a
means of reducing the bitterness of pharmacological drugs in tablet form, and it
has been used for livestock feed as a means of reducing feeding time. Other
products NHDC can be found in may include a wide variety of alcoholic beverages
(and nonalcoholic), savoury foods, toothpaste, mouthwash and condiments such
as ketchup and mayonnaise.
NHDC in pure form is found as a white substance not unlike powdered sugar.
In food it is used as a flavour enhancer in concentrations of around 45 parts
per million (ppm) and as an artificial sweetener at around 15-20 ppm.
Research has shown that at strengths of around and above 20 ppm,
NHDC can produce side effects such as nausea and migraine.
This is not widely documented, however is unquestionably known within the
food science communities that have worked with the product, and many recommend
wearing a surgical mask when handling pure NHDC.
.....................................................................................................................................
Certificate of Analysis
Items
Specification
Appearance
Fine white powder(Relate to Purity)
Odor
Characteristic
Taste
Characteristic
Paiticle size
Pass 80 mesh
Loss on drying
≤5%
Heavy metals
<10ppm
As
<1ppm
Assay
Result
Neohesperidosyl dihydrochalcone
≥99%
Total Plate Count
<1000cfu/g
Yeast & Mold
<100cfu/g
E.Coli
Negative
Salmonella
Negative
Molecular Structure :
About Us - Top Products- Partner with Us - Contact Us - Help - Sitemap
ChemNet is a registered trademark of Zhejiang NetSun Co., Ltd.
