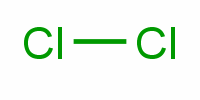Chlorine
Category: Inorganic chemicals

CAS NO: 7782-50-5 EC NO: 231-959-5 Molecular Formula: Cl2 Molecular Weight: 70.906 Specification: InChI: InChI=1/Cl2/c1-2 Product description:
Elemental chlorine is a gas of yellow greenish color and of characteristic pungent smell. Physically it is 2.5 times heavier than air, moderately soluble in water (about 2.3 L chlorine at ambient conditions in 1 L of water giving a 0.5 % solution of chlorine water) and easily to be liquified by raising pressure (approx 6.8 bar at 20癈). Liquified chlorine is an orange yellow low viscous liquid.
Chlorine is a highly reactive element which does not exist by itself in nature, but only combined with other elements, usually as common salt (sodium chloride). It is one of the most common elements in nature, even more plentiful than carbon. During the last century, scientists have found vast numbers of ways to take advantage of chlorine's useful properties in processes and products. Today, it has many uses important to health, safety, environment, and economy. Chlorine is essential to modern chemical industry and to modern society, too, with most of all chemical processing depending on this element. It allows the efficient use of raw materials and energy in the production of numerous compounds which would be difficult or impossible to synthesize using other pathways.
Synonyms: Bertholite;Chloor;chlore;Chlorine [UN1017] [Poison gas];Chlorine gas;cloro;dichloran;dicloran;Industrial Liquid Chlorine; Molecular Structure: