Home > Offer to Sell > Pharmaceuticals and Biochemicals > Vitamin, amino acids and coenzymes > L-Alanine CAS No : 56-41-7
L-Alanine CAS No : 56-41-7
Inquiry
| Post Date: | May 29,2013 |
| Expiry Date: | May 29,2014 |
| Detailed Description: |
Cas No. :56-41-7
Quantity: 20Metric Tons Specs:98.5% to 101.5% Payment Method: TT/LC L-Alanine CAS No : 56-41-7 Medicine grade Food Grade Amino Acids L-Alanine USP26 / CH3CH(NH2)COOH English name: L-Alanine CAS No : 56-41-7 Molecular formula: C3H7O2N Molecular Weight: 89.063 Structure:CH3CH(NH2)COOH Property: White powder Alanine, or L-alanine, is an amino acid that helps the body convert the simple sugar glucose into energy and eliminate excess toxins from the liver. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein, and are key to building strong, healthy muscles. Alanine has been shown to help protect cells from being damaged during intense aerobic activity, when the body cannibalizes muscle protein to help produce energy. Alanine is crucial for preserving balanced levels of nitrogen and glucose in the body, which it does through a series of chemical actions called the alanine cycle. During the alanine cycle, any excess amino acids (proteins) in cells or tissues are transferred to a receptor molecule called pyruvate, which is produced by the breakdown of glucose. The pyruvate is then converted to alanine and transferred to the liver. The liver extracts nitrogen from alanine and converts some of it back into pyruvate, which can then be used to produce more glucose. Any excess nitrogen is then converted into urea and passed out of the body during urination. This cycle, glucose-yruvate, helps supply the body with the energy it needs to support cellular life. It also ensures that a constant supply of pyruvate is available to allow the synthesis of glucose and amino acids in the body. Alanine plays a key role in maintaining glucose levels and thus energy supplies in the body. Epstein-Barr virus and chronic fatigue syndrome have been linked to excessive alanine levels and low levels of tyrosine and phenylalanine. Alanine may help regulate blood sugar as well. Research has found that for people with insulin-dependent diabetes, taking an oral dose of L-alanine effectively prevents nighttime hypoglycemia. Alanine is a nonessential amino acid, which means that a healthy body is able to manufacture its own supply of this substance. However, all amino acids may become essential (requiring dietary supplementation) if the body is for some reason unable to produce them. People with low-protein diets or eating disorders, liver disease, diabetes, or genetic conditions that cause Urea Cycle Disorders (UCDs), may need to take alanine supplements to avoid a deficiency. Low levels of alanine have been found in patients with hypoglycemia, diabetes, and hepatitis. It is not known at this time if alanine deficiency is the cause or result of these diseases. The body must have alanine to process the B vitamins so necessary for good health, especially vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) and vitamin B6 (pyridoxine). Because fluid in the prostate gland contains alanine, it has been theorized that this amino acid may help treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a condition in which the prostate becomes enlarged and causes urination discomfort. In one study, participants with BPH took 780 milligrams of alanine, glycine, and glutamic acid per day for two weeks, then 390 milligrams of these three amino acids for the next two and a half months, and saw a significant reduction in symptoms. Good sources of alanine are meat, poultry, eggs, dairy products, and fish. Some protein-rich plant foods like avocado also supply alanine. There are also a number of supplements containing alanine available on the market. However, keep in mind that taking any one amino acid could upset the balance of nitrogen in the body, and make it harder for the liver and kidneys eliminate waste. People with liver or kidney disease should consult a physician before taking any amino acid supplement. Applications: L-alanine is a pharmaceutical raw material of compound amino acid injection and oral liquid medicines. Also widely used as an additive material in the oral solution of amino acids as well as beverages, food, wine, spices, oils, cured meat products, pickles, it also play a preservative role. Specifications: Item Specification( USP26) Results State of solution (tranamittance) Not less than 98.0% 99.2% Specific rotation [α]D20 +13.7°to +15.1° +14.1° Identification Compare the infrared absorption spectrum of the sample with that of the standard by potassium bromide disc method Conforms Chloride(Cl) Not more than 0.05% Less than 0.05% Iron(Fe) Not more than 0.003% Less than 0.003% Heavy metals(Pb) Not more than 0.0015% Less than 0.0015% Arsenic (As2O3) Not more than 0.00015% Less than 0.00015% Other amino acid Chronmatographically Not detectable Conforms Loss on drying Not more than 0.2% 0.12% Residue on ignition (sulfated) Not more than 0.15% 0.07% Organic volatile impurities Conforms Conforms PH 5.5 to 7.0 6.3 Assay 98.5% to 101.5% 99.20% Conclusion: Compliant with the specification of AJI97 |
| CAS Registry Number: | 56-41-7 |
| Synonyms: | ;L-alanine-12C3;2-Aminopropanoic Acid;H-Ala-OH;L-2-Aminopropionic acid;Ala;2-Amino-Propionic Acid;Alanine;L-Alpha-Alanine; |
| Molecular Formula: | C3H7NO2 |
| Molecular Weight: | 89.09 |
| Molecular Structure: | 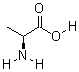
|
| Safety Description: | S24/25:; |
| Company: | Yuancheng Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd Hubei [ China ] |
| Contact: | Lupin |
| Tel: | +862768886724 |
| Fax: | +862788048077-899 |
| Email: | ycgsales02@ycphar.com |
-
Disclaimer statement:The information and data included above have been realized by the enterprises and compiled by the staff, and are subject to change without notice to you. The Chemnet makes no warranties or representations whatsoever regarding the facticity, accuracy and validity of such information and data. In order to ensure your interest, we suggest you chose the products posted by our gold suppliers or VIP members.