Cas No. :84082-34-8
Quantity: 2Metric Tons
Specs:Anthocyanidins 25%
Payment Method: L/C,T/T,Western Union,Escrow
Botanical Name: Vaccinium myrtillus L., Vaccinium Uliginosum L..
Product Specification:
Anthocyanidins 25% ( by UV)
Anthocyanins Anthocyanosides >36% (by HPLC)
Active Ingredient: 100% Bilberry
Appearane: Fine powder
Color: Dark Violet
Part of the plant used: Fruit
Extract method: Grain alcohol
Test method: UV
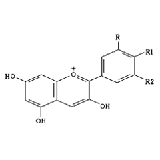
Molecular formula: C27H31O16
Molecular weight: 611
Molecular structure:
Solubility: Soluble in water and ethanol
Safety evaluation: innocuous
What is it?
Bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus)is found natively in Europe, northern Asia, Greenland, Western Canada, and the Western United States It occurs in the wild on heathlands and acidic soils.
Bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus)has been used for nearly 1,000 years in traditional European medicine. Herbal supplements of V. myrtillus (bilberry) on the market are used for circulatory problems, as vision aids, and to treat diarrhea and other conditions.
In cooking, the bilberry fruit is commonly used for the same purposes as the American blueberry: pies, cakes, jams, muffins, cookies, sauces, syrups, juices, candies and so on. Since bilberries are more fragrant, and have more concentrated flavor and vitamins (like all more natural wild fruit varieties), they are especially well suited for making cough syrups and bilberry wine
How does it work?
Anthocyanosides are the pharmacologically active constituents of bilberries. They consist of a backbone known as anthocyanidin which is bound to one of three sugars: arabinose, glucose, or galactose. Five different anthocyanidins in bilberry produce more than fifteen different anthocyanosides. The fresh bilberry fruit contains an anthocyanoside concentration of 0.1 to 0.25 percent.
Bilberry extract reduces UVA-induced oxidative stress in HaCaT keratinocytes: a pilot study.
Biofactors. 2008; Department of Medical Chemistry and Biochemistry, Palack?University, Olomouc, Czech Republic.
Exposure to UVA radiation is known to cause many adverse biological effects by inducing the stricken cells to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS). In recent years the use of botanicals has received considerable interest in the skin protection. Bilberry fruit contains several polyphenols with strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. In this study we evaluated potential UVA preventive effect of V. myrtillus fruit extract (VME; anthocyanins, 25% w/w) in HaCaT keratinocytes. Pre-treatment or post-treatment of HaCaT with VME resulted in attenuation of UVA-caused damage. Application of the extract significantly reduced UVA-stimulated ROS formation in keratinocytes. VME also prevented/reduced UVA-caused peroxidation of membrane lipids and depletion of intracellular GSH. The observed cytoprotective effect may be linked to the antioxidant activity of the plant constituents, namely anthocyanins.
Benefit and medical uses
The benefit of bilberry rests mostly on its ability to provide substances that are beneficial for eye health. It may benefit those who have macular degeneration or are predisposed to a cataract. Phenolic compounds in bilberry are of benefit as antioxidants.
Function:
-Protect and regenerate rhodopsin and cure the eye diseases;
-Prevent the cardiovascular diseases;
-Antioxidant and anti-aging;
-Treatment for mild inflammation of the mucous membranes of mouth and throat;
-Treatment for diarrhea, enteritis, urethritis, cystitis and virosis rheum epidemic, with its antiphlogistic and bactericidal action.