Chlorfenapyr 98%TC insecticide manufacturer in China
-
Post Date:
May 06,2020 -
Expiry Date:
May 06,2021 -
Detailed Description:
Cas No. :122453-73-0 Quantity: 1000Kilograms
Specs:98%TC
Price:10-20 USD Kilograms
Payment Method: T/T or L/C
APPLICATIONS
Biochemistry Oxidative removal in vivo of the N-ethoxymethyl group generates the active species, which is a mitochondrial uncoupler.Mode of action Insecticide and acaricide with mainly stomach and some contact action. Exhibits good translaminar but limited systemic activity in plants.
Uses Control of many species of insects and mites, including those resistant to carbamate, organophosphate and pyrethroid insecticides and also chitin-synthesis inhibitors, in cotton, vegetables, citrus, top fruit, vines and soya beans. Among pests resistant to conventional products which are controlled by chlorfenapyr are Brevipalpus phoenicis (leprosis mite), Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Colorado potato beetle), Helicoverpa spp., Heliothis spp., Plutella xylostella (diamond-back moth) and Tetranychus spp. Also control of many species of structural and household Formicidae (especially Camponotus, Iridomyrmex, Monomorium, and Solenopsis), Blattellidae (especially Blatta, Blattella, Periplaneta and Supella spp.), Kalotermitidae (especially Incisitermes) and Rhinotermitidae (especially Reticulitermes, Coptotermes, Heterotermes) at use rates of between 0.125 to 0.50% a.i. w/w. Phytotoxicity No phytotoxicity observed at field use rates.
product Name
Chlorfenapyr
Molecular Formula
C15H11BrClF3N2O
Molecular Weight
407.6128
CAS Registry Number
122453-73-0
Density
1.53g/cm3
Boiling point
443.5°C at 760 mmHg
Refractive index
1.559
Flash point
222°C
Vapour Pressur
4.6E-08mmHg at 25°C
Application
It can kill wide range of harmful insect, has good effect to prevent and control 70 kinds of harmful insects in lepidoptera, Coleoptera, and Homoptera, especially has unique effects on against some insects tolerant with some insecticides such as cole moth, sugar beet noctuid, limabean pod borer, thrips Carmine spider mite, Prodenia litura(Fabricius) and Liriomyza sativae(Blanchard).
-
CAS Registry Number:
122453-73-0 -
Synonyms:
;STALKER;4-BROMO-2-(4-CHLOROPHENYL)-1-(ETHOXYMETHYL)-5-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)-1H-PYRROL-3-CARBONITRILE;97% Chlorfenapyr TECH;Pirate;Alert;Sunfire;Citrex;Intrepid;4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-ethoxymethyl-5-trifluoromethylpyrrole-3-carbonitrile;4-bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-ethoxymethyl-5-trifluoromethyl-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile;Chlorfenapyr bulk drug; -
Molecular Formula:
C15H11BrClF3N2O -
Molecular Weight:
407.6128 -
Molecular Structure:
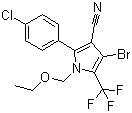
-
Hazard Symbols:
T:Toxic;
N:Dangerous for the environment;
-
Risk Codes:
R22:;
R23:;
R50/53:;
-
Safety Description:
S13:;
S36/37:;
S45:;
S60:;
S61:;
-
Company:
Zhengzhou Labor Agrochemicals Co.,Ltd. [ China ] -
Contact:
Sabrina Wan -
Tel:
+86-371-66813168/66813580 -
Fax:
+86-371-66819620 -
Email:
rd@pesticidechina.com