Green Tea Extract
-
Post Date:
Oct 28,2024
-
Expiry Date:
Oct 28,2025
-
Detailed Description:
Cas No. :989-51-5
Green Tea P.E.
Botanic Extracts
General Information
Product Name: Green Tea P.E.
Botanical Source: Camellia sinensis
Part of Plant Used: Leaves
Classification: Plant / Herb Extracts
Extract Solvent: Ethyl Ester and Hydro-alcohol
Products List (COA against request)
Product Standard Test
Green Tea Extract 40%
(Decaffeinated) >40% Polyphenols
20~25% Catechins
<3% Caffeine/<1% Caffeine UV-VIS
HPLC
HPLC
Green Tea Extract 50% >50% polyphenols
25~30% catechins
7~9% caffeine UV-VIS
HPLC
HPLC
Green Tea Extract 60% >60% polyphenols
30~35% catechins
7~9% caffeine UV-VIS
HPLC
HPLC
Green Tea Extract 60%
(Decaffeinated)
>60% polyphenols
>30% catechins
<3% caffeine/<1% Caffeine UV-VIS
HPLC
HPLC
Green Tea Extract 70% >70% polyphenols
40~45% catechins
7~9% caffeine UV-VIS
HPLC
HPLC
Green Tea Extract 80% >80% polyphenols
>50~55% catechins
7~9% caffeine UV-VIS
HPLC
HPLC
Green Tea Extract 90% >90% polyphenols
>60% catechins
<7~9% caffeine UV-VIS
HPLC
HPLC
Green Tea Catechins 60%
(Decaffeinated)
>90% polyphenols
>60% catechins
<1% caffeine UV-VIS
HPLC
HPLC
Green Tea Catechins 70% >95% polyphenols
>70% catechins
7~9% caffeine UV-VIS
HPLC
HPLC
Green Tea Catechins 70%
(Decaffeinated)
>95% polyphenols
>70% catechins
<1% caffeine UV-VIS
HPLC
HPLC
Green Tea Catechins 80%
(Decaffeinated)
>98% polyphenols
>80% catechins
<1% caffeine/<0.5% caffeine UV-VIS
HPLC
HPLC
Green Tea EGCg 10% EGCg
20% EGCg
30%EGCg
50%EGCg
60%EGCg
95%EGCg HPLC
HPLC
HPLC
HPLC
HPLC
HPLC
Green tea Theanine 20~40% HPLC
Green Tea Caffeine 10%~99% HPLC
Physical
Appearance: Dark brown powder
Odor: Characteristic
Particle Size: 100% Pass 80 mesh
Bulk Density: 30-55g/100ml
Storage:
In a cool and dry place. Keep away from direct strong light.
Packaging:
25kg/drum
Shelf Life:
Maximum 24 month when stored unopened provided proper storage conditions are maintained
Herb Information
Name: Green Tea
Biological Name: Camellia sinensis
Other Names: Green Tea
Parts Used: Leaves
Active Compounds:
Green tea contains volatile oils, vitamins, minerals, and caffeine, but the active constituents are polyphenols, particularly the catechin called epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). The polyphenols are believed to be responsible for most of green tea's roles in promoting good health.
Research demonstrates that green tea guards against cardiovascular disease in many ways. Green tea lowers total cholesterol levels and improves the cholesterol profile (the ratio of LDL cholesterol to HDL cholesterol), reduces platelet aggregation, and lowers blood pressure.
The polyphenols in green tea have also been shown to lessen the risk of several types of cancers, stimulate the production of several immune system cells, and have antibacterial properties-even against the bacteria that cause dental plaque.
History:
According to Chinese legend, tea was discovered accidentally by an emperor 4,000 years ago. Since then, traditional Chinese medicine has recommended green tea for headaches, body aches and pains, digestion, depression, immune enhancement, detoxification, as an energizer, and to prolong life. Modern research has confirmed many of these health benefits.
Remedies For:
Green tea is useful for:
Cancer risk reduction
Gingivitis (periodontal disease)
High cholesterol
Hypertension (high blood pressure)
Hypertriglyceridemia (high triglycerides)
Immune function
Infection
Most of the studies of the effect of the green tea have been focused on its cancer-causing and cancer-protecting aspects. Green tea polyphenols are potent antioxidant compounds. They are more potent antioxidants than vitamin E and vitamin C.
Green tea may also increase the activity of the antioxidant enzyme. A number of animal studies have shown that green tea polyphenols may offer significant protection from cancer. It is believed that they do so by blocking the formation of cancer-causing compounds such as nitrosamines, suppressing the activation of carcinogens, and detoxifying or trapping cancer causing agents.
Green tea is believed to have the greatest effect on cancers of the gastrointestinal tract such as stomach, small intestine, pancreas, and colon; lung cancer; and estrogen related cancers including most breast cancers.
It is interesting to note that green tea prevents cancer, whereas black tea increases the risk of certain cancers such as cancer of the rectum, gallbladder, and endometrium.
Description:
All teas (green. black, and oolong) are derived from the same tea plant, Camellia sinensis. The difference is in how the plucked leaves are prepared.
The tea plant has long been cultivated in China. It is an evergreen shrub or tree that can grow to a height of 30 feet, but is usually maintained at a height of 2 to 3 feet by regular pruning. The hairy leaves of the tea plant are used both as a social and medicinal beverage. The parts used are the leaf bud and the two adjacent young leaves together with the stem, broken between the second and the third leaf. Older leaves are considered inferior in quality.
Green tea, unlike black and oolong tea, is not fermented, so the active constituents remain unaltered in the herb. It is produced by lightly steaming the fresh cut leaf. Green tea is very high in polyphenols with potent antioxidant and anticancer properties.
Dosage:
Much of the research documenting the health benefits of green tea is based on the amount of green tea typically drunk in Asian countries-about three cups per day (providing 240-320 mg of polyphenols).
To brew green tea, 1 teaspoon of green tea leaves are combined with 250 ml (1 cup) of boiling water and steeped for three minutes. Tablets and capsules containing standardized extracts of polyphenols, particularly EGCG, are available; some are decaffeinated and provide up to 97% polyphenol content-which is equivalent to drinking four cups of tea.
-
CAS Registry Number:
989-51-5
-
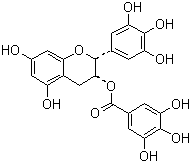
Synonyms:
;EGCG;(2R,3R)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3-yl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate;Green Tea Extract Powder;;Green Tea;Green Tea P.E;Green Tea Extract;Green tea extract Polyphenols;Green tee extract;Tea Polyphenols;Tea polyphenol;Tea Polyphenol (TP98);
-
Molecular Formula:
C22H18O11
-
Molecular Weight:
458.3717
-
Molecular Structure:
-
Company:
Rishon Biochem Co., Ltd
[ China ]
-
Contact:
Lei Cheng
-
Tel:
00868386661786
-
Fax:
00868382566283
-
Email:
info@rishonbiochem.com
Inquiry
