Mulberry leaves extract
-
Post Date:
Apr 14,2025 -
Expiry Date:
Apr 14,2026 -
Detailed Description:
Cas No. :19130-96-2 Quantity: 2Metric Tons
Specs:1-Deoxynojirimcin 12:1
Payment Method: L/C,T/T,Western Union,Escrow
Mulberry Leaves Extract 1-DNJLatin Name: Morus albaCAS No.: 19130-96-2Active Ingredient: 1-DeoxynojirimcinSpecifications: 12:1Test Method: TLCMulberry Leaves Extract Morus alba 1-DeoxynojirimcinMulberry leaves have long been used in Chinese medicine for the prevention and treatment of diabetes; they contain compounds that suppress high blood sugar levels.
Mulberry Fights Arterial Plaque
Scientists in Japan have pinpointed a number of biologically active compounds in extracts of the leaves of the white mulberry, Morus alba, a plant that silkworms are crazy about. 1 Not that the silkworms care, but the mulberry-leaf extract turns out to be effective in suppressing the progression of atherosclerosis, the buildup of cholesterol-rich plaque in our arteries. 2 It does this, apparently, by inhibiting the oxidation of LDL-cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein, the ¡°bad cholesterol¡±), which is a major factor in the development of atherosclerotic plaque.The Japanese researchers reached this conclusion based on their observations of the antioxidant effects of the mulberry extract on LDL-cholesterol taken from both rabbits and humans. They believe that the agents primarily (but not exclusively) responsible for this effect are two closely related compounds, isoquercitrin and astragalin. The former contains, as part of its molecular structure, the well-known antioxidant flavonoid quercetin, which is found in many foods and in a variety of nutritional supplements.In studying the antioxidant effects of the whole mulberry-leaf extract and, separately, of the compound isoquercitrin, as well as of the compound quercetin (which is not found as such in mulberry), the researchers observed that all were effective but that isoquercitrin was somewhat less effective than the same amount of quercetin. They also reported, however, that when isoquercitrin is ingested (by mice), it is largely metabolized to quercetin. Thus, although quercetin is not found in mulberry, mulberry is still a good source for it (and the silkworms still couldn't care less).ProfileBotanical resouce: mulberry leaf, Morus alba L.Latin Name: Folium Mori, Ramulus MoriPart of Plant Used: LeafActive Ingredient: 1-Deoxynojirimycin (1-DNJ)Specifications: 1%~20%Testing Method: HPLCCAS: 19130-96-2Molecular Formula: C6H13NO4Molecular Weight: 163.17Appearance: Brown PowderMake sure that you don't miss your chance toSource the latest innovative productsGet Free SampleUnconditional refund if unqualifiedKeep up to date with the latest trendsTest and analyze your ingredients free of chargeEnjoy All-inclusive packages visit to OHIDescriptionMorus alba, known as white mulberry, is a short-lived, fast-growing, small to medium sized mulberry tree, the species is native to northern China, and is widely cultivated and naturalized elsewhere. Extract derived from the leaves of the mulberry tree may yield health benefits when used medicinally.About 1-deoxynojirimycinMulberry leaf has a substance called moranoline (1-deoxynojirimycin) that inhibits an enzyme in the intestinal tract (alpha-glucosidase) involved in the digestion of carbohydrates. Moranoline holds back complex carbohydrates, starches, maltose and sucrose from breaking down into glucose.Propertiesantihyperglycemic, antioxidant and anti-glycationBenefitsBlood Sugar Balance,prevent diabetes mellitusLiver and Lung RemedyWeight lossApplicationMedicine ,cosmeitcs ,dietary supplement ,food aditive , food for livestock,tea
-
CAS Registry Number:
19130-96-2 -
Synonyms:
;Deoxynojirimycin;(2r,3r,4r,5s)-2-hydroxymethyl-3,4,5-trihydroxypiperidine;1,5-dideoxy-1,5-imino-d-glucito;1,5-dideoxy-1,5-imino-d-glucitol;1-deoxynojirimicin;1-deoxy-nojirimyci;5-amino-1,5-dideoxy-d-glycopyranose;5-dideoxy-5-amino-d-glucopyranos;5-piperidinetriol(2r-(2alpha,3beta,4alpha,5beta))-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4;(2R,3R,4R,5S)-2-(hydroxymethyl)piperidine-3,4,5-triol; -
Molecular Formula:
C6H13NO4 -
Molecular Weight:
163.1717 -
Molecular Structure:
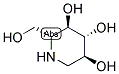
-
Company:
Hunan Huakang Biotech Inc [ China ] -
Contact:
Bunny Zhang -
Tel:
0731-88809323 -
Fax:
0731-88809325 -
Email:
sales11@huakangsw.com