Trichlorfon/ dipterex/ trichlorphon 97%TC insecticide China supplier
-
Post Date:
May 04,2020 -
Expiry Date:
May 04,2021 -
Detailed Description:
Cas No. :52-68-6 Quantity: 1000Kilograms
Specs:97%TC
Price:10-20 USD Kilograms
Payment Method: T/T or L/C
Common name
Trichlorfon/ dipterex/ trichlorphon
Chemical name
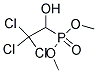
Dimethyl (2,2,2-trichloro-1-hydroxyethyl)phosphonate
CAS No
52-68-6
Molecular formula
C4H8Cl3O4P
Description
1.Melting Point:78.5°C
2.Vapour Pressure:13.33(100°C)
3.Molecular weight:257.45
4.Density:1.73g/cm3
5.Solubility (20°C) : In water 120g/L , toluene 20-50g/L, dichloromethane ,
isopropanol > 200g/L
Toxicity
ReviewsJECFA 54, FAO/WHO 30, 31 (see part 2 of the Bibliography).
IARC ref. 30 class 3
Oral Acute oral LD50 for male and female rats c.250 mg/kg.
Skin and eye Acute percutaneous LD50 (24 h) for male and
female rats >5000 mg/kg. Not irritating to skin and eye (rabbits).
Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male and female rats >2.3 mg/l air (aerosol).
NOEL (2 y) for rats 100, for mice 300 mg/kg diet; (4 y) for dogs 50 mg/kg diet.
ADI (JECFA) 0.02 mg/kg b.w. [2000]; (JMPR) 0.01 mg/kg b.w. [1978].
Toxicity class WHO (a.i.) II; EPA (formulation) II
EC classification Xn; R22| R43
Mode of action
Non-systemic insecticide with contact and stomach action.
Function
Insecticidal control in agriculture, horticulture, forestry,
food storage, gardening, households, and animal husbandry.
In particular, control of Diptera, Lepidoptera, Hymenoptera, Hemiptera,
and Coleoptera on many crops. For agricultural uses, applied at
300-1200 g/ha. Also used to control household pests such as flies,
cockroaches, fleas, bed bugs, silverfish, ants, etc.; as a fly bait
in farm buildings and animal houses; and for control of
ectoparasites on domestic animals.
-
CAS Registry Number:
52-68-6 -
Synonyms:
;((2,2,2-trichloro-1-hydroxyethyl)dimethylphosphonate);(1-Hydroxy-2,2,2-trichloroethyl)phosphonic acid, dimethyl ester;(1-hydroxy-2,2,2-trichloroethyl)-phosphonicacidimethylester;(2,2,2-Trichloro-1-hydroxyethyl)phosphonate, dimethyl ester;(2,2,2-trichloro-1-hydroxyethyl)-phosphonicacidimethylester;[(2,2,2-Trichloro-1-hydroxyethyl) dimethylphosphonate];1-Hydroxy-2,2,2-trichloro-ethyle phosphonate de dimethyle;1-hydroxy-2,2,2-trichloro-ethylephosphonatededimethyle;Trichlorfon;dimethyl (2,2,2-trichloro-1-hydroxyethyl)phosphonate;dimethyl [(1R)-2,2,2-trichloro-1-hydroxyethyl]phosphonate;dimethyl [(1S)-2,2,2-trichloro-1-hydroxyethyl]phosphonate;Chlorophos; -
Molecular Formula:
C4H8Cl3O4P -
Molecular Weight:
257.4367 -
Molecular Structure:
-
Hazard Symbols:
Xn:Harmful;
N:Dangerous for the environment;
-
Risk Codes:
R22:;
R43:;
R50/53:;
-
Safety Description:
S2:;
S24:;
S37:;
S60:;
S61:;
-
Company:
Zhengzhou Labor Agrochemicals Co.,Ltd. [ China ] -
Contact:
Sabrina Wan -
Tel:
+86-371-66813168/66813580 -
Fax:
+86-371-66819620 -
Email:
rd@pesticidechina.com