Vitamin B12
-
Post Date:
Nov 18,2017
-
Expiry Date:
May 17,2018
-
Detailed Description:
Cas No. :68-19-9
Quantity: mass in stockKilograms
Specs:Red Powder
Price:negotiable USD Kilograms
Payment Method: T/T, Western Union,Moneygram and Bitcoin.
Description:
Cyanocobalamin is a synthetic (man-made) form of vitamin B12. Naturally occurring vitamin B12 is found in fish, seafood, milk, egg yolk and fermented cheeses. Vitamin B12 is essential to the development of healthy blood cells, nerve cells, and proteins in the body and for the normal metabolism of fats and carbohydrates in the body. Lack of vitamin B12 can result in anemia, stomach problems, and nerve damage.
Cyanocobalamin treats or prevents vitamin B12 deficiency and a resulting type of anemia, called pernicious anemia. Pernicious anemia occurs in patients who do not have enough vitamin B12 in their diet (e. G., strict vegetarians) or who cannot adequately absorb the vitamin due to a defect or disease of the stomach or intestines.
Vitamin B12 is a cyanide ion substituted cobalamin derivative (cyanocobalamin) with the presence of cobalt mineral at 6 position. Vitamin B12 is the only vitamin which contains metal ion (trivalent cobalt). Cobalamin is sometimes defined as the synonym of Vitamin B12, although they are not same compound but closely related compounds to fulfill folic acid role. Vitamin B12 is typically any substituted cobalamin derivative having similar biological activity. Hydroxocobalamin (abbreviated OHCbl), a cobalamin derivative in which the substituent is a hydroxyl group, is called vitamin B12.
Vitamin B12 is a water soluble with a key role in the normal functioning of the and , and for the formation of . It is one of the eight . It is normally involved in the of every of the body, especially affecting synthesis and regulation, but also synthesis and energy production.
Vitamin B12 is the name for a class of chemically-related compounds, all of which have vitamin activity. It is structurally the most complicated vitamin. of the basic structure of the vitamin can only be accomplished by , but conversion between different forms of the vitamin can be accomplished in the human body.
A common synthetic form of the vitamin, , does not occur in nature, but is used in many pharmaceuticals, supplements and as food additive, due to its stability and lower cost. In the body it is converted to the physiological forms, and , leaving behind the , albeit in minimal concentration. More recently, methylcobalamin and, adenosylcobalamin can also be found in more expensive pharmacological products and food supplements. The utility of these is presently debated.
Historically, vitamin B12 was discovered from its relationship to the disease , which is an autoimmune disease that destroys parietal cells in the stomach that secrete intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor is crucial for the normal absorption of B12, therefore, a lack of intrinsic factor, as seen in pernicious anemia, causes a vitamin B12 deficiency. Many other subtler kinds of , and their biochemical effects, have since been elucidated.
Functions:
1. To promote the development of red blood cells and mature, make the body hematopoiesis functionary in normal, and prevent pernicious anemia.
2. To maintain the nervous system health.
3. It can increase the utilization rate of folic acid, promote carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism;
4. It has the role of amino acids with activation and can promote the nucleic acid biosynthesis, and can promote protein synthesis, it plays an important role in the infant's growth.
5. It is fatty acid metabolism, and can make fat, carbohydrate, protein be proper used by body.
6. To eliminate irritability, focus your attention, improve memory and balance.
7. It is nervous system function sound indispensable vitamin, a kind of nerve tissue in the formation of lipoprotein
Weight Loss
Vitamin B12 injections has been said to help in weight loss for the average person as well as competitive athletes and bodybuilders. Although there is really no concrete proof that vitamin B12 injections help with in weight loss, anecdotal evidence suggests it certainly aids in the absorption process of other substances that do.
Many weight loss centers offer B12 vitamin injections as a component of their weight loss plan. Those that have received vitamin B12 injections say that it provides extra energy and boosts their metabolic rate, which aids in losing surplus fat regardless of their other lifestyle choices, and whether or not they are competitive athletes or simply engage in routine exercise.
Athletes take vitamin B12 injection for the same energy boost and for better performance and also to aid in recovery from exercise sessions, for a mood boost, for concentration, and as a way to boost the immune system.
Vitamin B-12 and Bodybuilding
Vitamin B-12 assists in metabolizing protein and fat. As a bodybuilder, you need the amino acids from the protein metabolism to repair and build your muscles and the fat as a source of energy. B-12 is also essential for the production of red blood cells, which are necessary for delivering oxygen to those muscles. This nutrient also supports healthy neurological function, which is needed for muscle control.
Dosage:
Most adults in the United States do not have a difficult time meeting their daily vitamin B-12 needs, according to the Office of Dietary Supplements. The recommended dietary allowance for vitamin B-12 is 2.4 mg a day. Your body does not store B-12, and it has a low level of toxicity. However, if you're not deficient, taking more vitamin B-12 than is recommended will not improve your energy or your workouts.
-
CAS Registry Number:
68-19-9
-
Synonyms:
;cyano-5,6-dimethylbenzimidazole-cobalamin;Cyanocobalamin;VB12;5,6-dimethyl-1-(3-o-phosphono-alpha-d-ribofuranosyl)-1h-benzimidazolmonoes;
-
Molecular Formula:
C63H88CoN14O14P
-
Molecular Weight:
1355.3652
-
Molecular Structure:
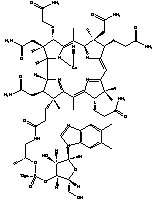
-
Safety Description:
S24/25:;
-
Company:
Hengyang Desen Science and Technology co., LTD.
[ China ]
-
Contact:
Eric yang
-
Tel:
+86-189-08446905
-
Fax:
-
Email:
Eric@desen-nutrition.com
Inquiry
