ABS
111Category: Polymers

CAS NO: 9003-56-9 EC NO: Molecular Formula: C15H17N Molecular Weight: 211.3022 Specification: InChI: InChI=1/C8H8.C4H6.C3H3N/c1-2-8-6-4-3-5-7-8;1-3-4-2;1-2-3-4/h2-7H,1H2;3-4H,1-2H2;2H,1H2 Product description:
ABS is derived from acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene.Chemically, this family of thermoplastics are called terpolymers, because they are made of three different monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene and styrene, to create a single material that draws on the best properties of all three. Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene ABS was introduced to the market in 1948, primarily as a result of activities that had taken place during the war years in the development of synthetic rubbers. Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene ABS possesses outstanding impact strength and high mechanical strength, which makes it suitable for use in tough consumer and industrial products, including: appliances, automotive parts, pipe, business machines and telephone components. In the 1960s, Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene ABS found wide outlet as a substrate for metallizing (i.e., applying a chrome-like metallic finish to the plastic) and appeared in such products as shower heads, door handles, faucet handles and automotive front grilles. A class of thermoplastic terpolymers including a range of resins, all prepared with usually more than 50% styrene [C 6 H 5 CHCH 2 ] and varying amounts of acrylonitrile [CH 2 CHCN] and butadiene [CH 2 CHCHCH 2 ]. The three components are combined by a variety of methods involving polymerization, graft copolymerization, physical mixtures and combinations thereof.Synonyms: 2-propenenitrile,polymerwith1,3-butadieneandethenylbenzene;ABS;abscopolymer;absresin;absresins;acrylonitrile,polymerwith1,3-butadieneandstyrene;acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrenecopolymers;Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styreneterpolymer;buta-1,3-diene; prop-2-enenitrile; styrene;Abs Resins; Molecular Structure: 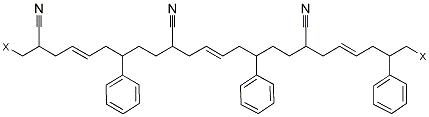
if you are sourcing ABS from South-Korea ,just feel free to inquire



