Product description:
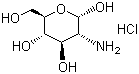
What is Glucosamine?
Other names: glucosamine sulfate, glucosamine sulphate, glucosamine hydrochloride, N-acetyl glucosamine, chitosamine
Glucosamine is a compound found naturally in the body, made from glucose and the amino acid glutamine. Glucosamine is needed to produce glycosaminoglycan, a molecule used in the formation and repair of cartilage and other body tissues. Production of glucosamine slows with age.
Glucosamine is available as a nutritional supplement in health food stores and many drug stores. Glucosamine supplements are manufactured in a laboratory from chitin, a substance found in the shells of shrimp, crab, lobster, and other sea creatures. In additional to nutritional supplements, glucosamine is also used in sports drinks and in cosmetics.
Glucosamine is often combined with chondroitin sulfate, a molecule naturally present in cartilage. Chondroitin gives cartilage elasticity and is believed to prevent the destruction of cartilage by enzymes. Glucosamine is sometimes combined with methylsulfonylmethane, or MSM, in nutritional supplements.
Why Do People Use Glucosamine?
Osteoarthritis
Glucosamine supplements are widely used for osteoarthritis, particularly knee osteoarthritis. In osteoarthritis, cartilage -- the rubbery material that cushions joints -- becomes stiff and loses its elasticity. This makes the joint prone to damage and may lead to pain, swelling, loss of movement, and further deterioration.
Since the body's natural glucosamine is used to make and repair joint cartilage, taking glucosamine as a nutritional supplement is thought to help repair damaged cartilage by augmenting the body's supply of glucosamine.
Other Conditions
Other conditions for which glucosamine is used include rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis), chronic venous insufficiency, and skin conditions, although further evidence is needed.
|
 CN
China Suppliers > jiasibiochem >
CN
China Suppliers > jiasibiochem >