Product description:
Detailed Information
Product Name
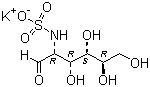
Glucosamine Sulfate Potassium
Brand Name
HS
Place of Origin
Zhejiang, China (Mainland)
Appearance
Crystalline white
Origin
Shellfish
Purity
98%-102%
Dosage Form
Powder
Usage
Food additives/ dietary supplement
Function
Alleviate gout and treat arthritis (especially osteoarthritis)
Package
Inner: double PE bags Outer: 25kg/fiber drum
MQO
25KG
Delivery Time
In a week from the date of PO
Testing Method
CPC&HPLC
Introdction of Chondroitin Sulfate
What is it?
Glucosamine sulfate is a naturally occurring chemical found in the human body. It is in the fluid that is around joints. Glucosamine is also found in other places in nature. For example, the glucosamine sulfate that is put into dietary supplements is often harvested from the shells of shellfish. Glucosamine sulfate used in dietary supplements does not always come from natural sources. It can also be made in a laboratory.
Glucosamine sulfate is commonly used for arthritis. Scientists have studied it extensively for this use. It is most often used for a type of arthritis called osteoarthritis. This is the most common type of arthritis.
Over the years, people have tried glucosamine sulfate for a variety of other uses. For example, it has been tried for glaucoma and for weight loss. But glucosamine sulfate has not been adequately studied for these uses. There is no proof that glucosamine sulfate is beneficial for these conditions.
There are different forms of glucosamine including glucosamine sulfate, glucosamine hydrochloride, and N-acetyl-glucosamine. These different chemicals have some similarities; however, they may not have the same effects when taken as a dietary supplement. Most of the scientific research done on glucosamine has been done on glucosamine sulfate. The information on this page pertains to glucosamine sulfate. For information on the other forms of glucosamine, see the specific pages for each of them.
Dietary supplements that contain glucosamine often contain additional ingredients. These additional ingredients are frequently chondroitin sulfate, MSM, or shark cartilage. Some people think these combinations work better than taking just glucosamine sulfate alone. So far, researchers have found no proof that combining the additional ingredients with glucosamine adds any benefit.
Glucosamine is also in some skin creams used to control arthritis pain. These creams usually contain camphor and other ingredients in addition to glucosamine. Researchers believe that any pain relief people may experience from these creams is due to ingredients other than glucosamine. There is no evidence that glucosamine can be absorbed through the skin.
Some glucosamine sulfate products are not labeled accurately. In some cases, the amount of glucosamine actually in the product has varied from none to over 100% of the amount stated on the product’s label. Some products have contained glucosamine hydrochloride when glucosamine sulfate was listed on the label.
How effective is it?
Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database rates effectiveness based on scientific evidence according to the following scale: Effective, Likely Effective, Possibly Effective, Possibly Ineffective, Likely Ineffective, Ineffective, and Insufficient Evidence to Rate.
How does it work?
Glucosamine sulfate is a chemical found in the human body. It is used by the body to produce a variety of other chemicals that are involved in building tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and the thick fluid that surrounds joints.
Joints are cushioned by the fluid and cartilage that surround them. In some people with osteoarthritis, the cartilage breaks down and becomes thin. This results in more joint friction, pain, and stiffness. Researchers think that taking glucosamine supplements may either increase the cartilage and fluid surrounding joints or help prevent breakdown of these substances, or maybe both.
Some researchers think the “sulfate” part of glucosamine sulfate is also important. Sulfate is needed by the body to produce cartilage. This is one reason why researchers believe that glucosamine sulfate might work better than other forms of glucosamine such as glucosamine hydrochloride or N-acetyl glucosamine. These other forms do not contain sulfate.
|
 CN
China Suppliers > jiasibiochem >
CN
China Suppliers > jiasibiochem >