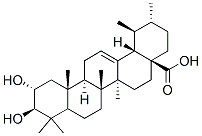
corosolic acid
111Category: Intermediates

CAS NO: 4547-24-4 EC NO: Molecular Formula: C30H48O4 Molecular Weight: 472.6997 Specification: InChI: InChI=1/C30H48O4/c1-17-10-13-30(25(33)34)15-14-28(6)19(23(30)18(17)2)8-9-22-27(5)16-20(31)24(32)26(3,4)21(27)11-12-29(22,28)7/h8,17-18,20-24,31-32H,9-16H2,1-7H3,(H,33,34)/t17-,18+,20-,21+,22-,23+,24+,27+,28-,29-,30+/m1/s1 Product description:
Corosolic acid Specification:corosolic acid 1%-20% Appearance:yellowish white powder
Application:
1. Diabetes:
Its ability to lower blood sugar is attributed to its corosolic acid, a triterpenoid glycoside, belived to facilitate glucose-transport into cells.
2. Weight loss:
A common ingredient in weight-loss supplements / products as a metabolic enhancer.
Others:
Used in the treatment of blood pressure, renal and immune system benefits. No toxicity has been identified.
Traditional uses include brewing tea from the leaves as a treatment for diabetes and hyperglycemia (elevated blood sugar).
The hypoglycemic (blood sugar lowering) effect of banaba leaf extract is similar to that of insulin which induces glucose transport from the blood into body cells.
Function:
Playing a role in regulating levels of blood sugar and insulin in the blood.
By keeping blood sugar and insulin levels in check, corosolic acid may be an effective supplement for promoting weight loss in certain individuals
Synonyms: (2alpha,3beta,5xi,18alpha)-2,3-dihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid;(2alpha,3beta)-2,3-dihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid; Molecular Structure: