Oolong tea extract
111Category: Pharmaceuticals and Biochemicals/Herbal Plant Extract

CAS NO: 989-51-5 EC NO: 283-519-7 Molecular Formula: C22H18O11 Molecular Weight: 458.3717 Specification: Polyphenols Catechins EGCg Caffeine 30% InChI: InChI=1/C22H18O11/c23-10-5-12(24)11-7-18(33-22(31)9-3-15(27)20(30)16(28)4-9)21(32-17(11)6-10)8-1-13(25)19(29)14(26)2-8/h1-6,18,21,23-30H,7H2/t18-,21-/m1/s1 Packing: 25kg/fiber drum I.D.42CM x H52CM Product description:
Oolong Tea ExtractProduct Item: OHI00000186Latin Name: Camellia sinensisCAS No.: 989-51-5Active Ingredient: Polyphenols Catechins EGCg CaffeineSpecifications: 30%Test Method: UV-VISOolong Tea Extract Camellia sinensis Polyphenols Catechins EGCg Caffeine
Oolong tea was actually shown to increase metabolism even more than green tea.5 Oolong tea increased resting energy needs by 10 percent compared to 4 percent for green tea. At first glance it might seem like drinking Oolong tea would be better than the green tea, but researchers found that the teas work for different reasons. Green tea is high in catechins and caffeine, while Oolong tea is high in polymerized polyphenols. The research suggests that by taking both teas, an even greater fat-burning effect can be achieved.Uses: pharmaceutical, health food Synonyms: EGCG;(2R,3R)-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3-yl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate;Green Tea Extract Powder;;Green Tea;Green Tea P.E;Green Tea Extract;Green tea extract Polyphenols;Green tee extract;Tea Polyphenols;Tea polyphenol;Tea Polyphenol (TP98); Molecular Structure: 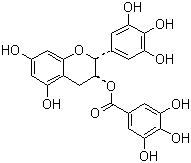
if you are sourcing Oolong tea extract from China ,just feel free to inquire



