Rhodiola rosea extract
111Category: Pharmaceuticals and Biochemicals/Herbal Plant Extract

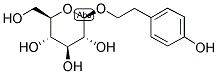
CAS NO: 10338-51-9 EC NO: 306-819-2 Molecular Formula: C14H20O7 Molecular Weight: 300.3044 Specification: Salidroside1-3%; rosavin1-6% InChI: InChI=1/C14H20O7/c15-7-10-11(17)12(18)13(19)14(21-10)20-6-5-8-1-3-9(16)4-2-8/h1-4,10-19H,5-7H2/t10-,11-,12+,13-,14-/m1/s1 Packing: 25kg/drum Product description:
Botanical Name: Rhodiola rosea
Product Specification: Salidroside1-3%; rosavin1-6%
Active Ingredient: Salidroside; rosavin
Appearane: Fine powder
Color: Yellow brown to red brown
Part of the plant used: root
Extract method: Grain alcohol
Test method: UV/HPLC
Molecular formula:

Molecular weight:300.3
Molecular structure:C14H20O7
Solubility: Soluble in ethanol
Safety evaluation: innocuous
What is it?
Rhodiola rosea may be effective for improving mood and alleviating depression. Pilot studies on human subjects showed that it improves physical and mental performance, and may reduce fatigue.
Rhodiola rosea's effects are potentially mediated by changes in serotonin and dopamine levels due to monoamine oxidaseinhibition and its influence on opioid peptides such as beta-endorphin, although these specific neurochemical mechanisms have not been clearly documented with scientific studies.
Rhodiola is included among a class of plant derivatives called adaptogens which differ from chemical stimulants, such asnicotine, and do not have the same physiological effects.
In Russia and Scandinavia, Rhodiola rosea has been used for centuries to cope with the cold Siberian climate and stressful life. Such effects were provided with evidence in laboratory models of stress using the nematode C. elegans, and in rats in which Rhodiola effectively prevented stress-induced changes in appetite, physical activity, weight gain and the estrus cycle.
Rhodiola has been used in traditional Chinese medicine, where it is called hóng jǐng tiān
Uses:
Rhodiola rosea (Rose root) has been used in traditional European medicine for over three thousand years, mainly as a tonic. Modern research has shown that it increases the body's resistance to any type of stress by regulating the body's hormonal response. Its use has been shown to have a protective effect upon the neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine in the brain. It improves neurotransmitter activity by inhibiting their enzymatic destruction and preventing their decline caused by excessive stress hormone release. Rose root also enhances the transport of serotonin's precursors into the brain and studies have shown that use of this herb can increase brain serotonin by up to 30%. The root is adaptogen. It has an enhancing effect upon physical endurance and sexual potency. A decoction of the flowers has been used to treat stomach aches and intestinal discomfort. The raw flowers have been eaten in the treatment of tuberculosis.
Function:
1. Anti-aging, anti-anoxia, anti-fatigue and anti-stimulus
2. Used as tonic and sexual elixir for both man and women
3. Resisting radiation and tumorUses: pharmaceutical, health food,cosmetic Synonyms: Rhodioloside;beta-d-glucopyranoside,2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl;glucopyranoside,p-hydroxyphenethyl;rhodosin;2-(4-HYDROXYPHENYL)ETHYL-BETA-D-GLUCOPYRANOSIDE;TWEEN 20 EXTRA PURE;RhodiolaCrenulataExtract;SALIDROSIDE(P);Rhodiola Rosea(3%Rosavin, 1%Salidroside);RhodiolaExtract;Rhodiola rosea extract;2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethyl beta-D-glucopyranoside;Smilax aristolochiaefolia, ext.;Rhodiola Extract;Rhodinal Rosea Extract;Rhodiola Rosea P.E.; Molecular Structure: