Bilberry Extract
111Category: Pharmaceuticals and Biochemicals

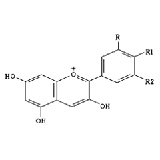
CAS NO: 84082-34-8 EC NO: 281-983-5 Molecular Formula: C27H31O16 Molecular Weight: 611.53 Specification: 1~36% Packing: 25kg/drum Product description:
Bilberry Extract 1~36%
Scientific Name(s): Vaccinum myrtillus L.
Family: Ericaceae (heaths)Common Name(s): Bilberries , bog bilberries , blueberries (variety of) , whortleberries
Uses of Bilberry
Dried bilberry tea is used internally to treat nonspecific diarrhea and topically to treat inflamed mouth and throat mucosa. Bilberry extracts may improve visual acuity and ability to adjust to changing light. Derivatives demonstrate vasoprotective, antiedema, and gastroprotective effects.Bilberry Dosing
Typical bilberry products are standardized to 25% anthocyanoside content. One recent study administered 160 mg of the extract tid to improve night vision.
Botany
Bilberry fruit originates from Northern and Central Europe and has been imported from parts of southeastern Europe. These black, coarsely wrinkled berries contain many small, shiny brownish-red seeds. They have a somewhat caustic and sweet taste.History
The historical uses of dried bilberry fruit include being a supportive treatment of acute, non-specific diarrhea when administered as a tea and serving as a topical decoction for the inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat.During World War II, British Royal Air Force pilots ate bilberry preserves before night missions in order to improve their vision. After the war, studies confirmed the folk beliefs that bilberry extracts could improve visual acuity and lead to faster visual adjustments between light (eg, glare) and darkness. 2 Some European physicians went on to recommend bilberry extracts for other eye complaints (eg, retinitis pigmentosa, diabetic retinopathy). Clinical studies, however, have not confirmed these therapeutic applications.
Chemistry
According to older studies, bilberry consists of up to 10% tannins, most of which are catechol tannins. In addition to tannins, bilberry contains anthocyanins, flavonoids, plant acids, invert sugars and pectins. The fresh fruit does not have the antidiarrhetic effects; therefore, it must be dried to obtain the tannins which come about by the condensation of the monomeric tannin precursors during the drying process.
Bilberry has been used for centuries, both medicinally and as a food in jams and pies. It is related to the blueberry and is native to Northern Europe. Bilberry fruit contains chemicals known as anthocyanosides, plant pigments that have excellent antioxidant properties. They scavenge damaging particles in the body known as free radicals, helping prevent or reverse damage to cells. Antioxidants have been shown to help prevent a number of long term illnesses such as heart disease, cancer, and an eye disorder called macular degeneration. Bilberry also contains vitamin C, which is another antioxidant.Not many studies have been done to examine bilberry specifically. Even fewer studies have been done in humans. Most of the suggestions about bilberry's effectiveness come from research on similar antioxidants, or from test tube and animal studies.
Chronic venous insufficiency
Bilberry extracts are used in Europe to treat this condition, which occurs when valves in veins in the legs that carry blood to the heart are damaged. Some studies have reported improvements in symptoms, but most of the studies were poorly designed.
Diabetes
Bilberry leaves have traditionally been used to control blood sugar levels in people with diabetes. Research shows that all berries help reduce the body's glucose response after eating a high sugar meal. Animal studies suggest bilberry may be effective for managing blood sugar levels. However, more research is needed. At this time, bilberry is not recommended to help manage diabetes.
Atherosclerosis
Animal studies have found that anthocyanosides may strengthen blood vessels, improve circulation, and prevent the oxidation of LDL ("bad") cholesterol, a major risk factor for atherosclerosis (plaque that blocks blood vessels, leading to heart attack and stroke). Research in people is needed.
Diarrhea and wounds
Bilberry has been used in European medicine for nearly a thousand years, primarily to treat diarrhea. The fruit contains tannins, substances that act as both an anti-inflammatory and an astringent (constricting and tightening tissues). Bilberry is believed to help people with diarrhea by reducing intestinal inflammation. No studies, however, have examined bilberry's use for diarrhea.
Vision
Anthocyanosides found in bilberry fruits may also be useful for people with vision problems. During World War II, British fighter pilots reported improved nighttime vision after eating bilberry jam. Studies have shown mixed results, however. Bilberry has also been suggested as a treatment for retinopathy (damage to the retina) because anthocyanosides appear to help protect the retina. Bilberry has also been suggested as treatment to prevent cataracts. However, studies are lacking in both areas.
Plant Description:
Bilberry is a perennial shrub that grows to about 16 inches in height. It has sharp edged, green branches and black wrinkled berries, which are ripe for picking in late summer. Bilberry is a relative of blueberry, cranberry, and huckleberry, and its fruit looks and tastes much like the American blueberry.What's It Made Of?:
The key compounds in bilberry fruit are called anthocyanosides. These compounds help build strong blood vessels and improve circulation to all areas of the body. They also prevent blood platelets from clumping together (helping to reduce the risk of blood clots), and they have antioxidant properties (preventing or reducing damage to cells from free radicals). Anthocyanidins boost the production of rhodopsin, a pigment that improves night vision and helps the eye adapt to light changes.Bilberry fruit is also rich in tannins, a substance that acts as an astringent. The tannins have anti-inflammatory properties and may help control diarrhea.
Available Forms:
You may eat bilberries fresh or dried, and you can make bilberry tea using fresh or dried berries. Bilberry extract should be standardized to contain 25% anthocyanidin. The extract contains the highest percentage of anthocyanosides, making it the strongest form of bilberry.How to Take It:
The use of herbs is a time honored approach to strengthening the body and treating disease. Herbs, however, can trigger side effects and can interact with other herbs, supplements, or medications. For these reasons, you should take herbs under the supervision of a health care provider.Pediatric
Bilberry may be used in children 2 years of age and older for the treatment of diarrhea, but only under the supervision of your doctor.
Adult
General: Based on most commercial bilberry products, the standardized bilberry extract contains 36% bilberry anthocyanosides.
The dosage is usually from 160 to 320 mg of bilberry extract. However, the website of University of Maryland suggests
dosage of 80-120 mg daily of bilberry extract (25% anthocyanidin) for general purpose.Diarrhea: 5 - 10 g of crushed dried bilberries in 150 mL (2/3 of a cup) cold water, brought to a boil for 10 minutes, then strained. Only dried bilberry should be used for diarrhea. Do not use for more than 4 days.
Eye conditions and circulation: 80 - 480 mg a day in 2 - 3 divided doses of standardized bilberry extract (with 25% anthocyanidin) in capsule form.
Precautions:
Bilberry fruit and extract are considered generally safe, with no known side effects. However, bilberry leaf and extract should not be taken in large quantities over an extended period of time because the tannins they contain may cause severe weight loss, muscle spasms, and even death. Taking bilberry may change the way other remedies, medicines, and even vitamins work, and using these products together may cause harmful effects.Possible Interactions:
Anticoagulants (blood-thinning medication) -- In theory, because the anthocyanosides in bilberry may stop blood from clotting, there may be an increased risk of bleeding if you take bilberry with blood thinning medication, including aspirin. The whole fruit may be safer in these instances. Ask your doctor before taking bilberry if you take blood thinning medication.Medication for diabetes -- Because bilberry appears to lower blood sugar, it could make the effects of diabetes medication stronger. Also, taking bilberry with other herbs that also lower blood sugar may result in hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Herbs that also lower blood sugar include ginger, ginseng, fenugreek, and garlic. Do not take bilberry if you take medications for diabetes.
Alternative Names:
European blueberry; Huckleberry; Vaccinium myrtillus; Vaccinium corymbosumUses: Bilberry extracts may improve visual acuity and ability to adjust to changing light. Derivatives demonstrate vasoprotective, antiedema, and gastroprotective effects. Synonyms: Cranberry P.E.;Billberry P.E.;Blue Berry P.E.; Molecular Structure: