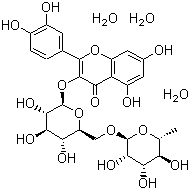
Rutin
111Category: Intermediates

CAS NO: 153-18-4 EC NO: 205-814-1 Molecular Formula: C27H30O16 Molecular Weight: 610.5175 Specification: InChI: InChI=1/C27H30O16/c1-8-17(32)20(35)22(37)26(40-8)39-7-15-18(33)21(36)23(38)27(42-15)43-25-19(34)16-13(31)5-10(28)6-14(16)41-24(25)9-2-3-11(29)12(30)4-9/h2-6,8,15,17-18,20-23,26-33,35-38H,7H2,1H3/t8?,15?,17-,18+,20-,21+,22?,23?,26+,27-/m0/s1 Product description:
Product Name: Rutin
Botanical Name: Sophora japonica Ait
Part Used: Buds
Main Active Ingredient: Rutin
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Specification:
95% Rutin NF11
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Active Ingredient: Rutin
CAS No.:153-18-4
Mol. Formula: C27H30O16.3(H2O)
Mol. Weight: 664.57
Structural formula:

----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Description:
The flavonoid rutin is a flavonol glycoside comprised of the flavonol quercetin
(see Quercetin) and the disaccharide rutinose. Many, if not most, of rutin's possible
activities can be accounted for, in part, by rutin's antioxidant activity. Rutin is a
phenolic antioxidant and has been demonstrated to scavenge superoxide radicals.
Rutin can chelate metal ions, such as ferrous cations. Ferrous cations are involved
in the so called Fenton reaction, which generates reactive oxygen species. Rutin
may also modulate the respiratory burst of neutrophils. The in vivo antioxidant activity
of rutin is most likely due to its' aglycone quercetin, to which it is metabolized following
ingestion. Although most studies show rutin to inhibit lipid peroxidation, a few studies
do not. Rutin may also help maintain levels of the biological antioxidant reduced
glutathione. Importantly, under certain conditions, rutin or its metabolite quercetin may
become a pro-oxidant. For example, nitrosation of rutin/ quercetin may produce a
pro-oxidant molecule that may have mutagenic potential.
Main Function:
1.Rutin is a bioflavonoid. It can enhance the absorption of Vitamin C; help to
relieve pain, bumps and bruises and has an antibacterial effect.
2.Rutin can promotes circulation, stimulate bile production, help to lower blood
cholesterol, and prevent cataracts.
3.Rutin is a phenolic antioxidant and has been demonstrated to scavenge superoxide
radicals.
4.Rutin can chelate metal ions, such as ferrous cations. Ferrous cations are involved in
the so-called Fenton reaction, which generates reactive oxygen species.
5.Rutin may also modulate the respiratory burst of neutrophils.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Specification Sheet
Items
Specification
Rutin
≥95% NF11 UV
Appearance
Fine yellow powder
Odor
Characteristic
Taste
Characteristic
Particle size
NLT 95% pass 80 mesh
Loss on drying
≤10%
Heavy metals
<10ppm
Irradiation
Irradiation Free
GMO
GMO Free
As
<1ppm
Pb
<3ppm
Total Plate Count
<10000cfu/g
Yeast & Mold
<300cfu/g
E.Coli
Negative
Salmonella
Negative
Physical Standard
CP2010
Chemical&Microorganism
StandardUSP34
Synonyms: C.I. 75730;(+)-Rutin Hydrate;Quercetin-3-rutinoside;Vitamin P;2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 6-O-(6-deoxyhexopyranosyl)hexopyranoside;2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl 6-O-(6-deoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl)-D-glucopyranoside;Rutin NF12;Rutin extract;Sophora Japonica Extract;Rurin Sophora Japonica Extract; Molecular Structure: